Introduction
Fingerprint evidence has stood the test of time as one of the most reliable and scientifically accepted forms of personal identification. Fingerprints and fingerprint experts play a crucial role in establishing facts, confirming identities, and upholding justice in both civil and criminal cases. Both fingerprint evidence and the expert opinion of a fingerprint examiner are essential in the legal field for proving the truth, identifying individuals, verifying documents, and assuring justice.The importance of fingerprint evidence and expert opinions has been further reinforced with the implementation of India’s new criminal laws, Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita (BNS), Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita (BNSS), and Bharatiya Sakshya Adhiniyam (BSA).
Fingerprint Analysis
Fingerprint analysis is the process of identifying and comparing the unique ridge patterns found on human fingers. Even among identical twins, these patterns vary from person to person and don’t change throughout the course of a person’s lifetime. A fingerprint expert is a trained forensic professional who specializes in collecting, developing, analyzing, comparing, and interpreting fingerprints for investigative and legal purposes.
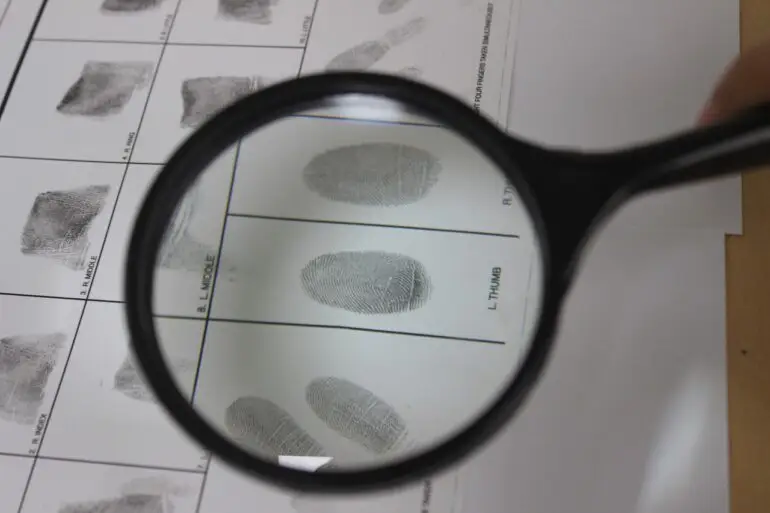

Fig 1. Examination of fingerprints
Legal Importance
Fingerprint evidence plays a critical role in legal investigations for the following reasons:
- Identification of Individuals: Fingerprints provide conclusive proof of identity, especially when other forms of identification are unavailable or disputed.
- Linking Suspects to Crime Scenes: Fingerprints recovered from objects at a crime scene (e.g., weapons, doors, documents) can confirm the presence of a suspect.
- Authentication of Legal Documents: Thumb impressions on property papers, affidavits, wills, and contracts can be examined to verify if they were genuinely signed or forged.
- Exoneration of Innocent Individuals: The absence of an individual’s fingerprints from a crime scene may support claims of innocence.
- Support in Civil Litigation: Fingerprint analysis is often used in property disputes, family inheritance claims, or disputed legal transactions to validate signatures or impressions.
Role of Fingerprint Experts in Legal Cases
Fingerprint experts act as scientific witnesses who analyze fingerprint evidence and provide expert opinions in courts of law. Their responsibilities include:
- Collecting fingerprints from crime scenes or documents
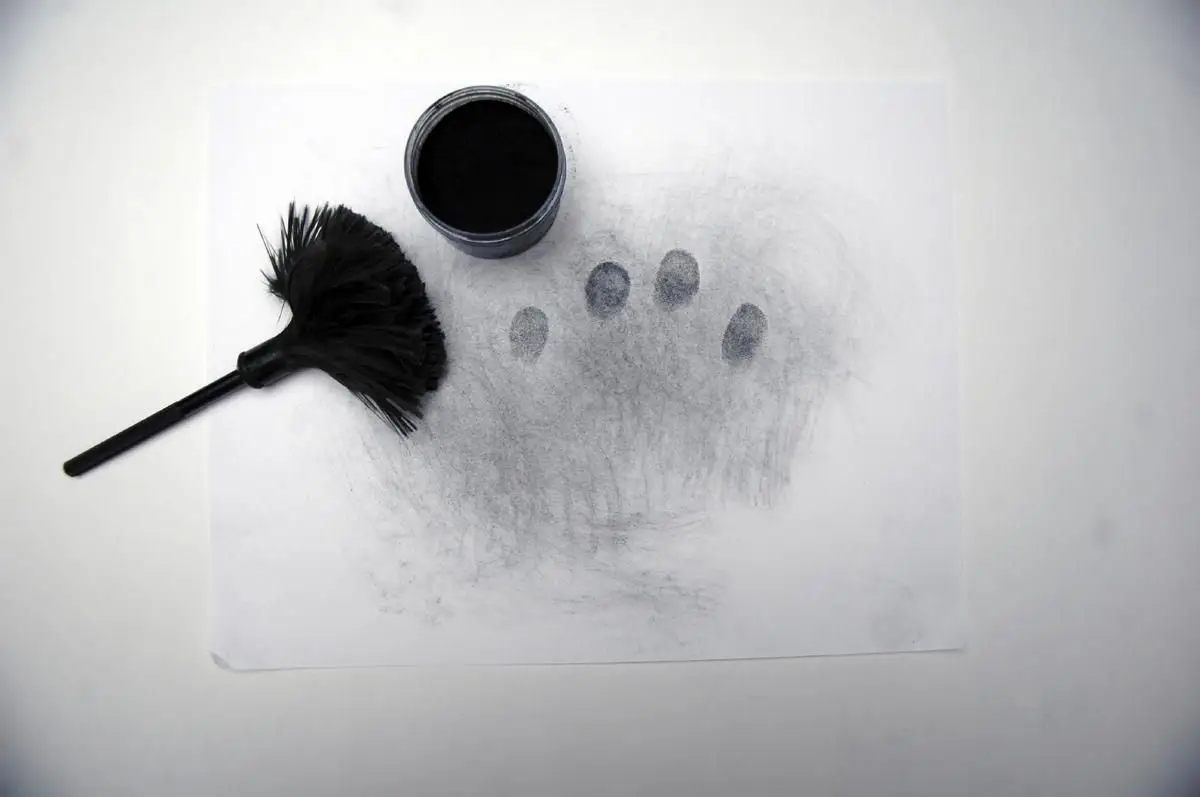
- Developing latent fingerprints using powder, chemical, etc
- Comparing questioned prints with known or specimen prints
- Preparing expert opinion reports for court submission
- Testifying as expert witnesses under oath
A fingerprint expert’s opinion often serves as decisive evidence in both civil and criminal trials.
Legal Provisions Related to Fingerprint Evidence in India
1. Bharatiya Sakshya Adhiniyam, 2023 (BSA) (Replaces the Indian Evidence Act, 1872).
This act defines the rules for admissibility of evidence in Indian courts.
Section 39 of the Bharatiya Sakshya Adhiniyam (BSA), 2023 (formerly Section 45 of the Indian Evidence Act) states that the opinion of a fingerprint expert is considered valid expert evidence in court. Judicial systems acknowledge the role of forensic experts in analyzing and interpreting fingerprint evidence in both criminal and civil cases.
2. Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita, 2023 (BNSS) (Replaces the Code of Criminal Procedure, 1973 – CrPC)
This act governs the procedural aspects of law, including investigation and evidence gathering.
Section 349 of the Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita (BNSS), 2023 (which replaces Section 311A of the CrPC) authorizes magistrates to order any individual, including the accused, to provide fingerprint, palm print, footprint, or other biometric samples for investigative purposes. This provision grants legal authority to law enforcement to obtain fingerprint evidence from suspects through proper judicial sanction to support the investigation3. The Criminal Procedure (Identification) Act, 2022 (Replaces the Identification of Prisoners Act, 1920)
This law governs the collection of biometric and behavioral measurements from convicts and persons in custody.
- This act allows the collection of fingerprints, palm prints, footprints, photographs, iris and retina scans, and other biological samples from:
- Persons convicted, arrested or detained under any preventive detention law.
- Any person ordered by a Magistrate.
- The data can be stored by National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) for up to 75 years.
4. Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita, 2023 (BNS) (Replaces the Indian Penal Code, 1860)
Fingerprints are frequently utilized in the investigation of crimes under BNS, even though the BNS does not specifically define fingerprint evidence. Examples of these crimes include:
|
Relevant BNS Sections
|
Use of Fingerprints in Investigation
|
|
Section 103 – Theft
|
Fingerprints at the crime scene (e.g., safe, lock, cabinet).
|
|
Section 111 – Robbery
|
Used to identify and link accused to stolen items or location.
|
|
Section 75 – Murder
|
Fingerprints on weapon, scene, or objects used in commission.
|
|
Section 69 – Forgery
|
Fingerprint comparison for disputed thumb impressions or documents.
|
|
Section 121 – Rape
|
For identification and linking presence of accused at the scene.
|
Common Types of Cases Include:
-
- Murder
- Theft and burglary
- Forgery and fraud
- Assault and kidnapping
- Civil Cases:
- Property disputes
- Will verification
- Marital or inheritance disagreements
- Corporate Investigations:
- Employee background verification
- Fraudulent document cases
- Identity verification
Admissibility of Fingerprint Evidence in Indian Courts
Under both old and new legal systems, fingerprint evidence has been consistently admissible in Indian courts. With modern forensic labs and trained experts, the evidentiary value of fingerprints has only increased.
Fingerprint experts submit their findings in well-documented reports and, when required, appear in court to explain their methodology and opinion. Courts give high credibility to expert testimony under Section 39 of the Bharatiya Sakshya Adhiniyam (BSA).
Training and Capacity Building for Fingerprint Analysis
With the growing demand for forensic professionals, institutions like Hawk Eye Forensic provide offline, hands-on training in fingerprint development, comparison, and report writing. Trainees learn practical techniques using real forensic tools and get exposure to actual case scenarios.
Conclusion
Fingerprint evidence continues to play a vital role in modern legal systems due to its scientific reliability, uniqueness, and ability to establish identity with precision. With the help of fingerprint experts and forensic science, the Indian legal system is now better equipped to deliver justice in a more transparent and technology-driven manner.
As forensic laws evolve and investigative methods modernise, the role of fingerprints and fingerprint experts becomes even more crucial in ensuring truth, fairness, and legal accountability.





Post comments (0)