Introduction: Why Ink Dating Attracts So Much Attention
In financial disputes, property conflicts, wills, and contract fraud cases, one common question often arises: “When was this document actually written?”
Many people assume that forensic science can precisely determine the exact date when ink was placed on paper. However, the reality is more complex. While forensic document examination provides scientific tools to evaluate ink, it does not always offer an exact calendar date.
This article explains what ink dating can realistically achieve, what it cannot, and why the subject is often misunderstood in legal proceedings.
What Is Ink Dating?
Ink dating refers to the scientific examination of ink to estimate whether:
-
The ink entries were made at the same time
-
Different parts of a document were written at different times
-
A signature was added later
-
The ink is relatively recent or older
It does not usually determine an exact day, month, or year of writing.
Instead, experts evaluate chemical composition, ink behavior, and aging characteristics to form an opinion within scientific limits.
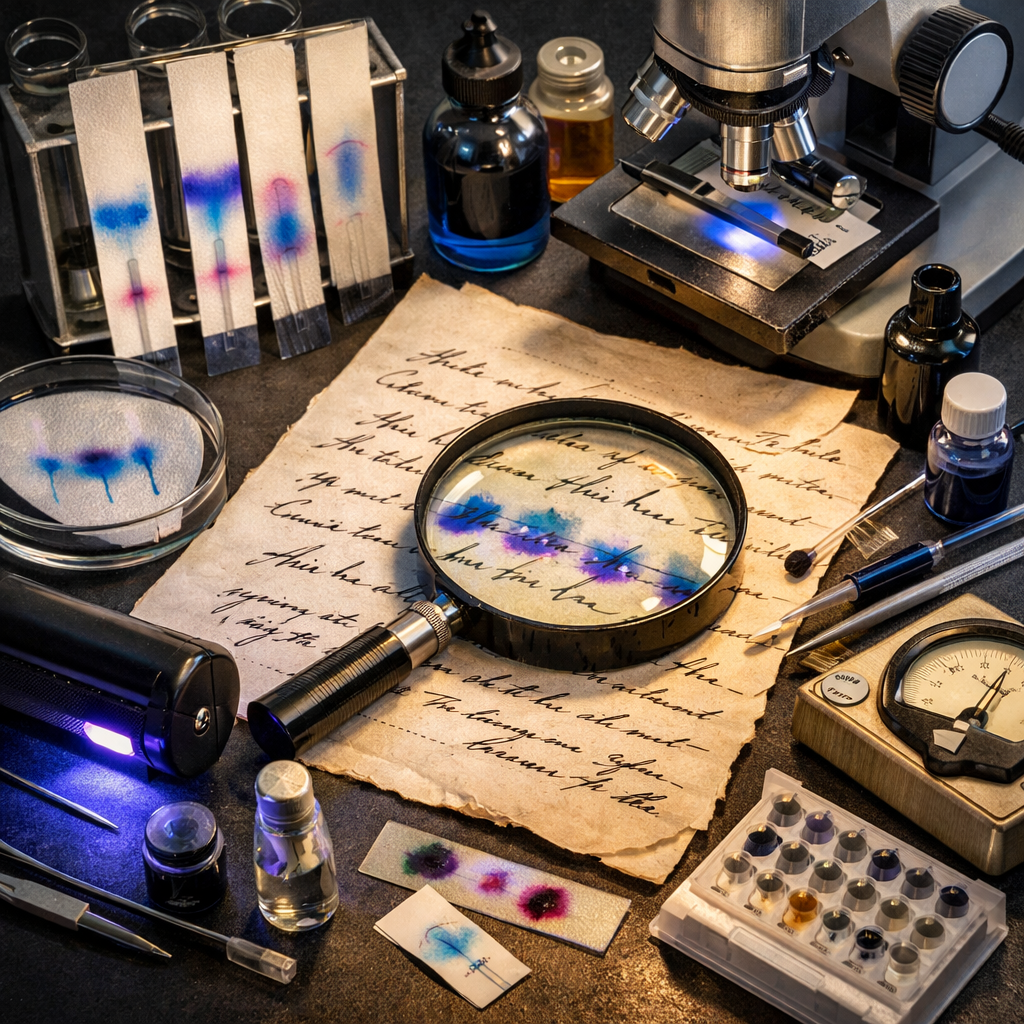
The Science Behind Ink Examination
Forensic experts rely on analytical techniques to study ink components. Some commonly used methods include:
1. Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC)
TLC separates dye components in ink. If two inks show different chemical patterns, they likely originate from different sources.
This technique helps answer questions such as:
2. Solvent Analysis (Ink Aging Studies)
Many ballpoint inks contain volatile solvents. Over time, these solvents evaporate. By analyzing solvent levels, experts may estimate whether ink is relatively recent.
However, environmental factors such as heat, humidity, and paper type significantly influence evaporation rates.
3. Instrumental Techniques
Advanced laboratories may use:
These methods provide more precise chemical analysis but still have interpretative limitations.
Myth vs Reality
Myth 1: Ink Dating Can Tell the Exact Date of Writing
Reality:
Forensic ink analysis rarely provides an exact date. It may indicate whether ink is recent or relatively old, but pinpointing a specific date is scientifically unreliable in most cases.
Myth 2: All Inks Age at a Predictable Rate
Reality:
Ink aging depends on multiple variables:
-
Storage conditions
-
Exposure to sunlight
-
Paper absorbency
-
Ink formulation
Therefore, two identical pens may show different aging behavior under different conditions.
Myth 3: Ink Dating Always Works in Court
Reality:
Courts scrutinize ink dating evidence carefully. Experts must clearly explain limitations and avoid overstating conclusions. Overconfident claims can weaken credibility.
Judges and lawyers increasingly demand scientifically validated methodologies and transparent reporting.
When Ink Dating Is Most Useful
Ink examination becomes particularly valuable when:
-
A signature is suspected to be added later
-
Dates appear altered
-
Multiple entries seem inconsistent
-
A will or agreement is challenged
-
Fraud is suspected in financial documents
Even when exact dating is not possible, identifying that entries were made at different times can significantly impact a case.
Limitations of Ink Dating
Despite technological advancements, ink dating has important limitations:
-
Lack of universal ink databases
-
Variability in ink formulations
-
Environmental influence on solvent evaporation
-
Limited sample size for destructive testing
-
Restricted access to advanced laboratory equipment
Because of these constraints, ink dating opinions are often expressed cautiously.
The Role of the Forensic Document Examiner
A qualified forensic document examiner does not rely on ink analysis alone. Instead, they combine:
-
Handwriting examination
-
Line sequence analysis
-
Indentation analysis
-
Paper examination
-
Printing characteristics
This holistic approach strengthens conclusions and reduces the risk of error.
Conclusion: Science Over Sensation
Ink dating is a powerful forensic tool, but it is not a time machine. While it can reveal whether entries were made at different times or with different inks, it rarely identifies an exact writing date.
Understanding the scientific boundaries of ink dating prevents unrealistic expectations and promotes responsible courtroom testimony.
In forensic document examination, accuracy and transparency matter more than dramatic claims.



Post comments (0)