Types of Digital Evidence Every Forensic Student Must Know
In the modern digital age, crimes rarely occur without leaving electronic traces. Therefore, digital evidence has become a crucial part of forensic investigations. From mobile phones to cloud storage, digital devices store valuable information that can help investigators reconstruct events. For this reason, every forensic student must clearly understand the different types of digital evidence and their role in criminal investigations and court proceedings.
This blog explains the main types of digital evidence that every forensic student should know, along with their forensic importance.
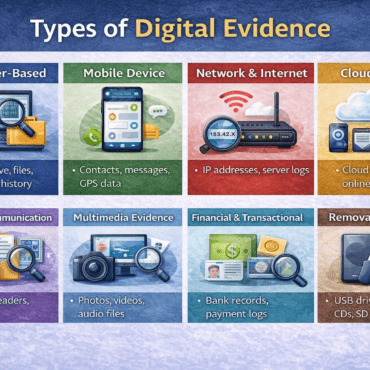
1. Computer-Based Digital Evidence
First and foremost, computers remain one of the most common sources of digital evidence. Desktop systems, laptops, and servers store large volumes of user data. As a result, investigators frequently examine computer systems during digital forensic investigations.
This type of evidence includes:
Moreover, deleted files may still exist in unallocated space. Therefore, proper forensic imaging and analysis are essential. Consequently, computer-based digital evidence often helps establish timelines and user activity.
2. Mobile Device Evidence
In addition to computers, mobile phones serve as powerful sources of digital evidence. Today, people use smartphones for communication, payments, navigation, and social networking. Therefore, mobile device evidence plays a major role in modern investigations.
Common examples include:
-
Call logs and contacts
-
Text messages and chat applications
-
Photos, videos, and audio recordings
-
Location data and GPS history
-
App usage information
However, mobile data changes rapidly. For this reason, investigators must isolate and preserve mobile devices as early as possible. As a result, forensic students must understand proper seizure and handling techniques.
3. Network and Internet-Based Evidence
Similarly, network and internet activity generate important digital evidence. This type of evidence is especially relevant in cybercrime cases such as hacking, online fraud, and identity theft.
Examples include:
-
IP addresses
-
Server and firewall logs
-
Chat records
-
Website access logs
-
Network traffic data
Although this evidence provides critical leads, it often exists for a limited time. Therefore, timely collection becomes extremely important. Consequently, forensic students should learn how network data supports digital investigations.
4. Cloud-Based Digital Evidence
With the growing use of cloud services, digital evidence is no longer limited to physical devices. Instead, cloud-based evidence exists on remote servers maintained by service providers.
This evidence includes:
However, cloud evidence introduces legal and technical challenges. For example, data access may depend on jurisdiction and service provider policies. Therefore, forensic students must understand both the value and limitations of cloud-based digital evidence.
5. Email and Communication Evidence
Furthermore, email communication remains a key source of digital evidence. Many cases involving fraud, harassment, and corporate crimes rely heavily on email data.
Email evidence includes:
Most importantly, email headers help trace the origin of messages. Therefore, forensic students should understand basic email header analysis and its investigative significance.
6. Multimedia Digital Evidence
Likewise, multimedia files often serve as important digital evidence. Investigators commonly recover images, videos, and audio recordings from phones, computers, and storage devices.
Examples include:
-
Crime scene photographs
-
CCTV footage
-
Voice recordings
-
Videos shared online
However, multimedia files can be easily edited or manipulated. For this reason, forensic examination focuses on metadata and file authenticity. As a result, forensic students must learn how experts detect tampering and verify originality.
7. Financial and Transactional Digital Evidence
In many investigations, digital financial records provide strong supporting evidence. Online transactions leave digital trails that help investigators track financial activity.
This type of evidence includes:
Therefore, such evidence proves especially useful in cases involving fraud, scams, and money laundering. Consequently, forensic students should understand how financial digital evidence supports criminal investigations.
8. Removable Media Evidence
Finally, removable storage devices often contain crucial digital evidence. These devices are portable and easy to conceal, which increases their forensic importance.
Examples include:
-
USB flash drives
-
External hard disks
-
Memory cards
-
Optical storage media
Because these devices are easily damaged or altered, investigators must handle them carefully. Therefore, proper imaging and documentation remain essential.
Importance of Understanding Digital Evidence
Overall, each type of digital evidence requires careful handling, documentation, and preservation. If investigators fail to follow proper procedures, courts may reject the evidence. Therefore, forensic students must understand not only how to identify digital evidence but also how to protect its integrity.
Moreover, digital evidence often supports other forensic findings. As a result, it strengthens investigations and improves the reliability of expert opinions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, digital evidence plays a vital role in modern forensic science. From computers and mobile phones to cloud data and financial records, each type of digital evidence contributes to the investigative process. Therefore, every forensic student must develop a strong understanding of these categories. With proper knowledge, training, and ethical handling, students can build a solid foundation for a successful career in digital forensics.



Post comments (0)