Introduction
In the ever-evolving world of cybersecurity, attackers are constantly finding new ways to bypass defenses. One of the most dangerous and sophisticated threats today is fileless malware—a stealthy type of malicious code that operates directly in a computer’s memory rather than leaving behind traditional files on disk.
For digital forensic investigators, this poses a serious challenge. Unlike conventional malware that leaves footprints in the form of executables, registry entries, or files on a hard drive, fileless malware is almost invisible. It thrives in volatile memory, making detection, analysis, and evidence collection highly complex.
This is where Fileless Malware Forensics comes in—a specialized branch of digital forensics that focuses on uncovering traces of malware that never existed as a traditional file.
What is Fileless Malware?
Fileless malware is a non-traditional attack method that:
-
Does not rely on files stored on the disk.
-
Operates in RAM (volatile memory).
-
Uses legitimate tools and processes (e.g., PowerShell, WMI, JavaScript) to execute malicious actions.
-
Often disappears when the system reboots, leaving minimal evidence behind.
Why Fileless Malware is So Dangerous
Traditional antivirus and intrusion detection systems rely heavily on signature-based detection and file scanning. Fileless malware cleverly avoids these by:
-
Not writing files to the disk.
-
Using trusted system processes (making them appear legitimate).
-
Frequently changing behavior (polymorphic in nature).
-
Eliminating itself upon reboot, leaving little evidence.
For cybercriminals, fileless malware is a perfect weapon—hard to detect, hard to trace, and devastatingly effective.
Forensic Challenges in Fileless Malware Investigations
Investigators face several roadblocks when dealing with fileless malware:
-
Volatility of Evidence
-
Absence of Disk Artifacts
-
Use of Legitimate Processes
-
Persistence Mechanisms
-
Encrypted Communications
Forensic Techniques for Investigating Fileless Malware
Despite these challenges, forensic experts have developed advanced methods to investigate fileless malware:
1. Live Memory Forensics
-
Capture volatile memory (RAM) using forensic tools before the system is powered down.
-
Tools: Volatility, Rekall, Belkasoft RAM Capturer.
-
Key focus: malicious processes, injected code, unusual DLLs, hidden threads.
2. Volatile Data Collection
-
Gather system snapshots, open network connections, process lists, and loaded modules.
-
Helps identify suspicious runtime behavior.
3. Behavioral Forensics
-
Monitor script activity, command execution, and unusual PowerShell commands.
-
Analyze logs for anomalous use of administrative tools.
4. Registry and Log Examination
5. Network Forensics
-
Capture and analyze network traffic to detect hidden communication with command-and-control (C2) servers.
-
Indicators: unusual outbound connections, DNS tunneling, or encrypted payloads.
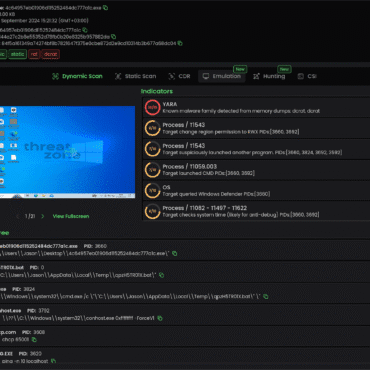
6. Sandbox and Emulation
7. Threat Intelligence Correlation
Real-World Cases of Fileless Malware Attacks
-
FIN7 / Carbanak Group – Used PowerShell-based fileless malware to steal millions from financial institutions.
-
APT32 (OceanLotus) – Used WMI scripting for persistence in espionage campaigns.
-
Kovter Malware – Notorious for fileless persistence via registry keys.
These cases highlight how sophisticated cybercrime groups prefer fileless techniques to avoid detection and extend attack lifespans.
Best Practices for Fileless Malware Forensics
-
Immediate Memory Acquisition – Always capture RAM before shutting down the system.
-
Log Retention Policies – Maintain detailed PowerShell, WMI, and Sysmon logs.
-
Baseline Analysis – Compare current system behavior with known clean baselines.
-
Threat Hunting – Proactively look for anomalies in scripts, processes, and memory.
-
Collaboration – Work with cybersecurity teams to integrate forensic findings into threat intelligence.
Conclusion
Fileless malware represents the next generation of cyber threats—stealthy, sophisticated, and devastatingly effective. Forensic experts face unique challenges due to the absence of traditional artifacts, but with the right tools, techniques, and expertise, these invisible attacks can still be uncovered.
At Hawk Eye Forensic, our certified experts specialize in advanced memory forensics, volatile data analysis, and live system investigations to detect even the most sophisticated fileless malware. We ensure that critical evidence is captured, analyzed, and presented lawfully for use in legal proceedings.




Post comments (0)