The SHA-256 hash algorithm is a key tool in the field of cryptography, respected for its dependability and extensive application in guaranteeing data integrity, authentication, and security. This thorough manual seeks to give readers a thorough grasp of the fundamentals of the SHA-256 hash algorithm by examining its functions, uses, advantages, and importance in the field of cybersecurity.
What is SHA-256?
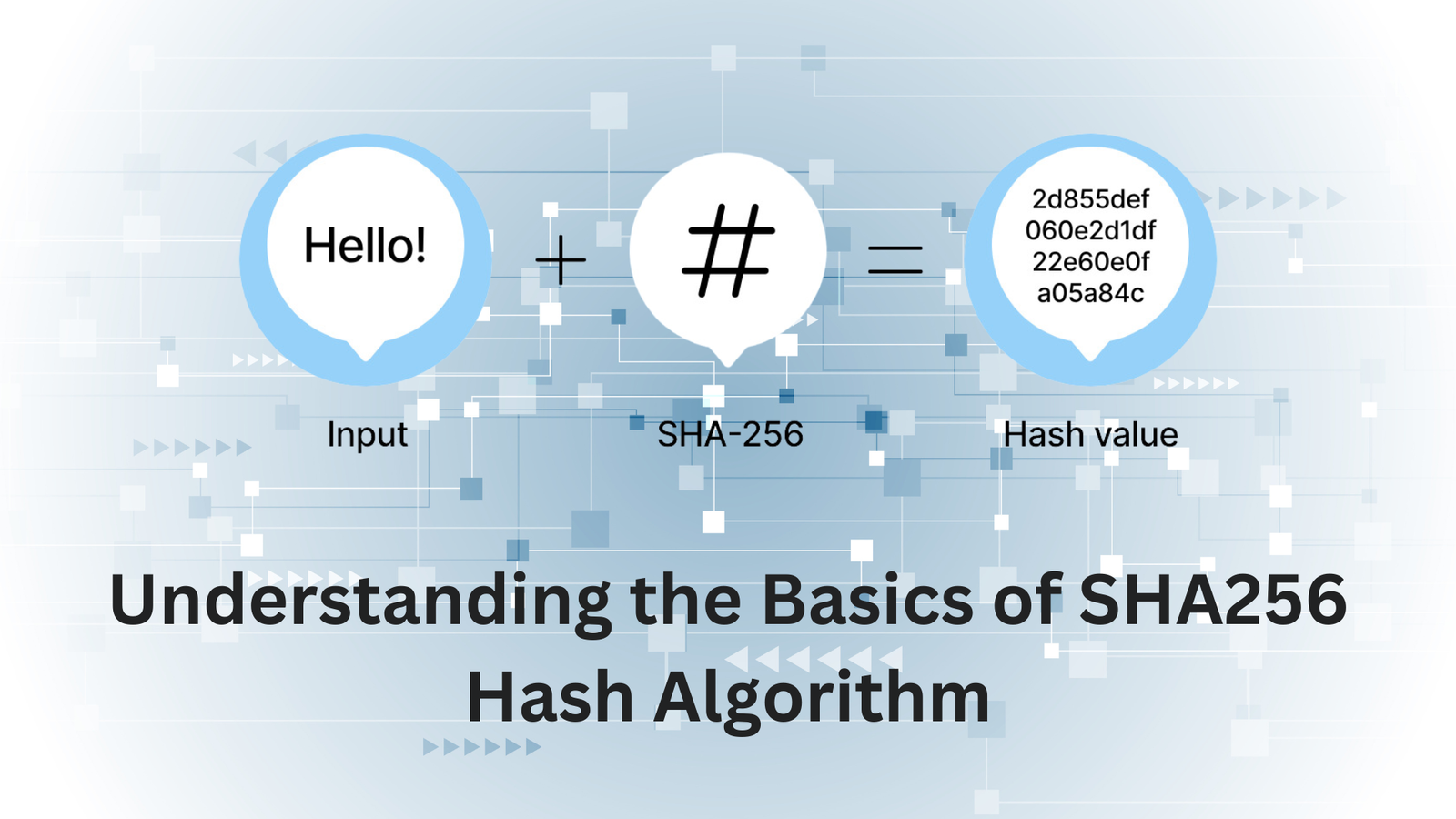
A member of the Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA) family, SHA-256 was created in the US by the National Security Agency (NSA). It produces a fixed-size, 32-byte, 256-bit hash value, which is commonly expressed as a 64-character string in hexadecimal. Because of SHA-256’s well-known resistance to collisions, various inputs always result in noticeably distinct hash values.
How Does SHA-256 Work?
- The operation of SHA-256 involves several intricate steps to derive a unique hash value from input data. Understanding its underlying process sheds light on its robustness and reliability:
- Message Padding: Input messages are padded to meet specific block size requirements, ensuring uniform processing.
- Initializing Constants: SHA-256 employs predefined constants for initialization, setting the initial hash values.
- Processing Blocks: The input message is divided into 512-bit blocks, undergoing a series of logical functions, rotations, and mixing operations.
- Compression Function: This function updates the hash state after processing each block, ensuring a uniformly distributed output.
- Finalization: After processing all blocks, the hash value is derived from the final state of the algorithm, producing the 256-bit hash output.
Applications of SHA-256
Digital Signatures: SHA-256 is widely used in digital signatures, providing assurance of the integrity and authenticity of electronic documents, software, and communications.
Data Integrity Verification: In various industries, SHA-256 is employed to verify data integrity, ensuring that transmitted or stored information remains unaltered.
Cryptographic Applications: SHA-256 serves as a crucial component in cryptographic protocols, secure communication channels, and authentication mechanisms.
Strengths of SHA-256
Collision Resistance: SHA-256 boasts exceptional collision resistance, making it computationally infeasible to find two distinct inputs that produce the same hash value.
Widely Adopted and Trusted: Its widespread adoption and inclusion in cryptographic standards by various organizations showcase the trust and reliability placed in SHA-256.
Conclusion
The SHA-256 hash algorithm stands as a cornerstone in modern cryptography, providing a robust means to ensure data integrity, authenticate information, and secure sensitive data against tampering or unauthorized access. Understanding the fundamentals of SHA-256, its operation, applications, and strengths is pivotal in leveraging its capabilities effectively for securing digital communication, data storage, and authentication mechanisms. As cybersecurity continues to evolve, SHA-256 remains an indispensable tool in safeguarding the integrity and confidentiality of data in today’s digital landscape.
- Exploring the Applications of SHA-Hash in Blockchain Technology
- Is SHA-Hashing Algorithm Still Secure in the Age of Quantum Computing?
- Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using SHA-Hashing Algorithm
- Future Perspectives: Enhancements and Evolutions of SHA-Hash Function
- Future Perspectives: Enhancements and Evolutions of SHA-Hash Function


Post comments (0)